Follow us on Telegram and on Instagram @humanresourcesonline for all the latest HR and manpower news from around the region!
share on
As part of the HR Jobs Transformation Map, several data points have been provided on the future of HR - such as HR roles most at-risk of being displaced by technology, and more.
Singapore's Ministry of Manpower (MOM) has dedicated the latest edition (26th) of the Jobs Situation Report to the HR function, and provided a summary of resources available to the HR community to lead workforce and workplace transformation.
The following are some of the support measures for HR professionals to leverage:
1. HR professionals can take up IHRP’s certification (Institute for HR Professionals); today, over 4,500 aspiring and existing HR professionals are IHRP-certified. They can also join IHRP’s Communities of Practices (e.g. IHRP COVID-19 Taskforce) or refer to its HR playbooks, with new sector-specific and thematic playbooks to be launched in the future.
2. Resources for businesses to strengthen their human capital practices are available, such as the Human Capital Diagnostic Tool (HCDT), or the HCDT Navigator, which is a free-to-use self-help version that can be completed within 30 minutes. They can also join the Corporate Partners Programme for networking.
3. The Human Resource Jobs Transformation Map (HR JTM), launched in December 2020, identifies key technology drivers and analyses technology’s impact on HR jobs over the next five years. [more details on this below]
4. Grant support under Productivity Solutions Grant (PSG) and the SME Start Digital Programme to encourage businesses to adopt HR technologies.
5. Recognising exemplary employers through Human Capital Partnership (HCP) Programme, led by the Tripartite Partners (MOM, SNEF, NTUC). There are currently about 600 HCPartners, who together employ more than 250,000 workers, of which more than 80% are locals. Amongst the HCPartners are five employment agencies: Cornerstone Global Partners, Dynamic Human Capital, Profile Search and Selection, Search Index, and SearchAsia Consulting.
For the benefit of the HR community, HRO has summarised some key aspects of the HR JTM, based on excerpts from the full report, below.
Most significant is the impact of technology on 27 roles in HR (such as CHRO, Head of Talent Management, Manager HRBP, Head of L&OD, Head of Performance & Rewards, and more).
The report lists out the key future skills required in each of these roles, provided in the table below:
 As the table above shows, each sub-function in HR has a set of function-specific skills, and a set of overarching cross-functional skills that are common to all 27 jobs, such as financial acumen, data-driven storytelling, agile mindset, and more.
As the table above shows, each sub-function in HR has a set of function-specific skills, and a set of overarching cross-functional skills that are common to all 27 jobs, such as financial acumen, data-driven storytelling, agile mindset, and more.
To view the infographic more clearly, head over to page 45 of the full report, or right-click the image above and select 'Open in a new tab'.
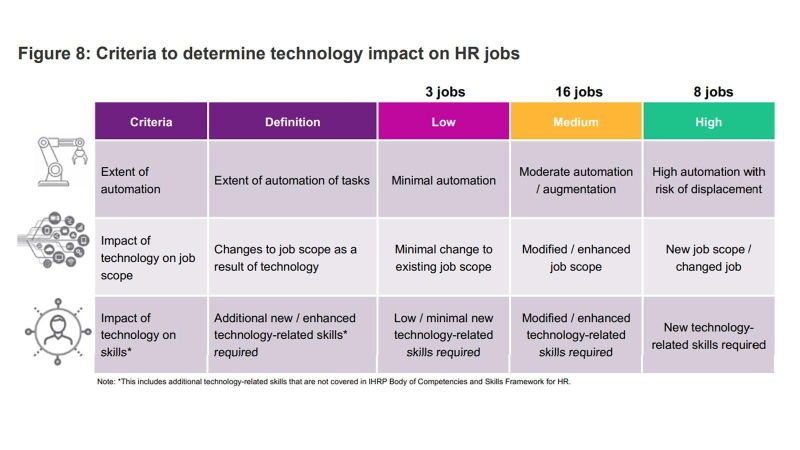
Also important to note is the impact of technology on jobs in HR - classified across jobs with high level of impact (of technology, thus highest at-risk), medium impact, and low impact. These jobs are detailed below:
Jobs with high level of impact
These jobs are at high risk of displacement or jobs that have a significantly new/changed job scope that requires new technology-related skills.
These jobs are largely operational in nature with a high volume of transactional processing and administrative tasks. For example, tasks such as first-line support and query handling, and other such variable and cognitive tasks that can be automated. A combination of RPA, chatbots, and AI / ML can be used to automate the above tasks.
An example: Associate, Learning and Organisation Development Today, the role includes maintenance of learning databases, coordination of training, collection of data and feedback etc. These tasks will be substituted by technology such as mobile applications, AI etc.
In the future, the role will need to support the evaluation and testing of platforms for communication, learning etc., and assess the effectiveness of learning programmes linked to the business metrics. This requires new skills in User Experience / User Interface Design, Omnichannel Communication, People Analytics etc
Jobs with medium level of impact
These jobs are augmented by technology, have an enhanced/modified job scope and require enhanced technology-related skills.
These jobs have a balance of strategic and operational elements. Tasks will require a moderate to high level of cognitive capability, human judgment, relationship building, and communication with stakeholders. Specific processes which have a defined process flow can be delivered through technology. The role will need to derive insights from the data generated from these processes.
An example: Manager, Talent Attraction Today, the role includes tasks such as execution of recruitment plans through sourcing, screening, assessments, onboarding, etc. Some of these tasks will be increasingly augmented by technology solutions such as AI / ML for initial sourcing, screening, and assessments, and AI/chatbots to enhance onboarding and candidate experience.
In the future, the role will work closely with business to develop a Talent Value Proposition (TVP) for multiple talent personas. Identification of talent will become more sophisticated due to competitive intelligence and market research. Also, the role will focus on delivering a seamless candidate experience through the use of technology solutions. This requires skills related to Talent Persona Design, Data-led Talent Acquisition, and Candidate Experience Design.
Jobs with low level of impact
These jobs will not experience significant change to their existing job scope and will not require many new technology-related skills.
Such roles are largely strategic in nature or rely significantly on relationship-building skills. For example, tasks such as influencing business leaders or formulation of talent strategies do not require deep technology-related skills, but instead a broader understanding of technology and talent trends.
An example: Head, HR Business Partner HRBPs guide business leaders on workforce strategy, develop tailored talent programmes, and lead implementation of these programmes for the business. Going forward, the role will drive business transformation through job redesign and strategic workforce planning and develop personalised programmes for different talent across businesses.
This will require new skills in the areas of strategic business and HR advisory, work architecture and job redesign, as well as strong data analysis skills. It will however require relatively less technology-related skills.
All images / Human Resource Jobs Transformation Map (HR JTM)
share on